Message Logger Service Documentation
Introduction
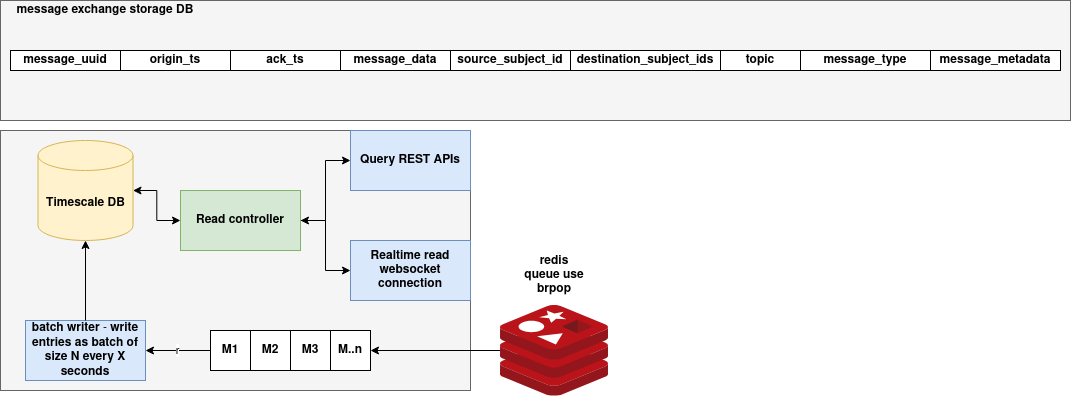
The Message Logger Service is a backend service that captures and persists message exchanges between distributed agents or services. It is designed for efficient, high-throughput message logging using Redis for ingestion and TimescaleDB for storage. The service includes:
- A Redis-based ingestion pipeline for buffering and batching.
- A PostgreSQL/TimescaleDB storage backend optimized for time-series data.
- REST APIs for querying messages by UUID or participant subject.
This service is suitable for use cases like audit logging, inter-service communication tracing, and message event monitoring.
Architecture
Message Log Schema
Messages are stored in the message_exchange table with the following schema:
| Column Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
message_uuid |
UUID | Unique identifier for the message (primary key). |
origin_ts |
TIMESTAMPTZ | Timestamp indicating when the message was created. |
ack_ts |
TIMESTAMPTZ | Timestamp indicating when the message was acknowledged. |
message_data |
JSONB | The actual payload of the message. |
source_subject_id |
TEXT | ID of the subject that sent the message. |
destination_subject_ids |
TEXT[] | List of IDs of the subjects that are the recipients. |
topic |
TEXT | Topic or channel under which the message was categorized. |
message_type |
TEXT | Type or classification of the message (e.g., "event", "alert"). |
message_metadata |
JSONB | Additional metadata related to the message. |
Batched Writing via Redis Consumer
The system uses a Redis-backed ingestion pipeline that buffers messages and writes them in batches to reduce write amplification and improve performance.
Process Overview
- Messages are published to a Redis list (configured via
Config.REDIS_QUEUE). - The
RedisConsumerclass listens to the Redis queue usingBRPOP. -
Received messages are:
-
Parsed into a tuple.
- Added to a buffer.
- When the buffer reaches a configured
BATCH_SIZEor after a specifiedBATCH_INTERVAL, the messages are bulk inserted into TimescaleDB viaINSERT ... VALUES.
This design ensures efficient ingestion while maintaining data integrity and reducing database I/O load.
REST APIs to Query Messages
The service exposes two REST endpoints via a Flask web server for retrieving message logs.
Get Message by UUID
Endpoint:
GET /messages/<message_uuid>
Description: Fetches a single message by its unique UUID.
Example:
curl http://localhost:5000/messages/123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000
Response:
{
"message_uuid": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000",
"origin_ts": "2025-05-27T10:30:00Z",
"ack_ts": "2025-05-27T10:30:01Z",
"message_data": {"text": "hello"},
"source_subject_id": "subject-A",
"destination_subject_ids": ["subject-B"],
"topic": "greetings",
"message_type": "chat",
"message_metadata": {"priority": "high"}
}
Get Messages by Subject ID
Endpoint:
GET /messages/subject/<subject_id>
Description: Fetches all messages where the given subject is either the sender or a recipient.
Example:
curl http://localhost:5000/messages/subject/subject-A
Response:
[
{
"message_uuid": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000",
"origin_ts": "...",
"ack_ts": "...",
...
},
{
"message_uuid": "456e7890-f12a-34d5-b678-526617183333",
"origin_ts": "...",
"ack_ts": "...",
...
}
]
WebSocket Server for Real-Time Updates
The service includes a WebSocket server that enables clients to receive message logs in real-time as they are published to Redis.
How It Works
- The server subscribes to a Redis pub/sub channel specified in
Config.REDIS_QUEUE. -
When a new message is published to Redis:
-
It is broadcast to all connected WebSocket clients.
- The server maintains active connections using an internal
clientsregistry.
WebSocket Endpoint
- Protocol: WebSocket (
ws://) - Port: Configurable in deployment environment
- Path: Root (
/) by default
Clients can connect using a standard WebSocket client to the exposed server address.
Example WebSocket Client
import asyncio
import websockets
async def listen():
uri = "ws://<websocket-host>:<port>"
async with websockets.connect(uri) as websocket:
while True:
message = await websocket.recv()
print("Received:", message)
asyncio.run(listen())
Replace <websocket-host> and <port> with the actual deployment address of the WebSocket server.
Internal Architecture
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
handler |
Handles WebSocket client connections. |
broadcast_message |
Sends new Redis messages to all active WebSocket clients. |
listen_to_redis |
Subscribes to Redis and listens for new messages. |
start_websocket_server |
Initializes both the WebSocket server and Redis listener. |
This component is useful for streaming dashboards or real-time monitoring tools that require instant visibility into new message events without polling APIs.